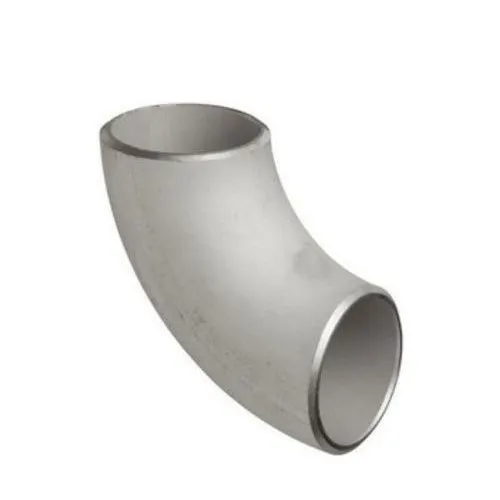

What is a butt weld elbow? A butt weld elbow is a type of pipe fitting used to change the
A lock nut, also known as a self-locking nut or prevailing torque nut, is a type of fastener designed to resist loosening under vibration, torque, or other external forces. Lock nuts employ various mechanisms to prevent unintentional loosening, ensuring that the nut remains securely fastened in its place.
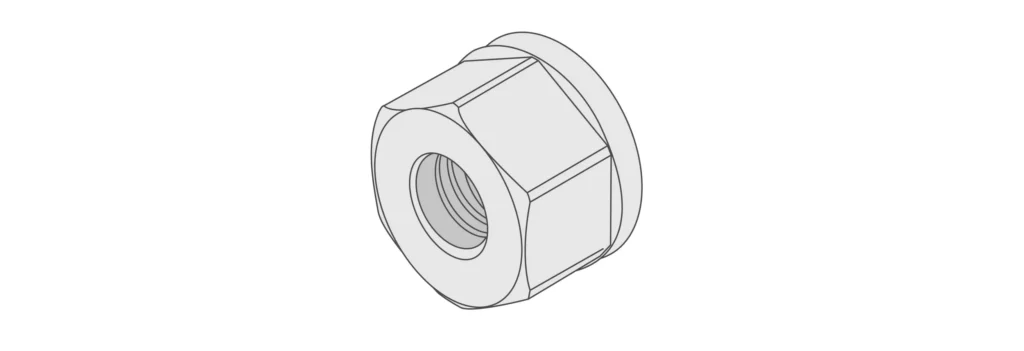
Friction Lock Nuts:
– Nylon Insert Lock Nuts: These nuts have a nylon ring or insert at the top of the nut’s threads. When the nut is tightened onto a bolt, the nylon insert creates friction, adding resistance against loosening due to vibration.
– Metal Lock Nuts: Some lock nuts utilize distorted threads or grooves to create interference, increasing friction between the nut and bolt threads, thus preventing loosening.
Positive Locking Nuts:
– Castle Nuts: These have slots or notches on the sides and require a cotter pin through the bolt’s hole to prevent rotation, ensuring the nut stays in place.
– Serrated Flange Nuts: Featuring serrations under the flange, these nuts grip the surface material when tightened, preventing loosening due to vibration.
When tightening a lock nut, it’s crucial to apply the recommended torque specified for the particular nut type. Over-tightening can damage the locking mechanism, while insufficient torque might lead to inadequate locking and potential loosening.
Lock nuts are available in various materials based on the application’s requirements:
– Steel: Commonly used for general-purpose applications due to its strength and affordability.
– Stainless Steel: Offers corrosion resistance, suitable for environments where rust or corrosion is a concern.
– Brass: Used in applications requiring non-magnetic properties or a more aesthetic appearance.
Hexagonal Lock Nuts (Standard Nuts):
– Diameter: Measure the distance across the flats of the nut’s hexagonal shape.
– Thread Pitch: Determine the number of threads per unit length (threads per inch or millimeter).
Lock Nut Sizes
• #00 – 10″
• M1.2 – M250
Other Types:
– For specialized lock nuts like nylon insert nuts or prevailing torque nuts, the measurements focus on the specific features of the locking mechanism rather than standard diameter and thread pitch.
Choosing the Right Lock Nut:
Selecting the appropriate lock nut depends on factors such as the application’s vibration levels, environmental conditions, torque requirements, and desired level of security against loosening.
When choosing a lock nut, consider the specific locking mechanism best suited for the application, the material compatibility, and the installation and tightening procedures to ensure a secure and reliable fastening solution.
ASME B18.16.3M:
This specification by the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) covers the dimensions, material requirements, and performance criteria for prevailing torque lock nuts. ASME B18.16.3M ensures the consistency and quality of lock nuts intended for mechanical and structural applications in the United States.
DIN Standards:
1. DIN 980: Specifies prevailing torque type all-metal prevailing torque lock nuts. It includes dimensions, materials, and mechanical properties to ensure proper performance in industrial applications.
2. DIN 6923: This standard covers hexagon nuts with an incorporated flange. DIN 6923 includes specifications for dimensions and tolerances for flanged hex nuts, ensuring compatibility with bolt threads.
3. DIN 985: Specifies prevailing torque type non-metallic insert lock nuts (nylon insert lock nuts). These nuts contain a nylon ring that provides resistance against loosening due to vibrations.
4. DIN 986: Similar to DIN 985, this standard outlines specifications for prevailing torque type all-metal insert lock nuts.
ISO Standards:
1. ISO 7042: Specifies prevailing torque type all-metal prevailing torque lock nuts with metric fine pitch threads. It covers dimensions, material requirements, and test methods to ensure proper functionality in various applications.
2. ISO 19513: Covers mechanical properties and performance specifications for prevailing torque all-metal hexagon thin nuts (metric series) with small widths across flats. It ensures their durability and resistance to loosening.
3. ISO 4161: Specifies prevailing torque type all-metal prevailing torque nuts with coarse pitch threads. It defines the dimensions, materials, and performance criteria for these nuts.
4. ISO 10511: Similar to ISO 7042, this standard covers prevailing torque type all-metal prevailing torque lock nuts with metric coarse pitch threads. It ensures uniformity in dimensions, materials, and performance.
5. ISO 7040: Specifies prevailing torque type all-metal prevailing torque nuts with reduced loadability. It includes dimensions, materials, and performance criteria for these lock nuts.
Each standard outlines specific requirements for different types of lock nuts, ensuring that they meet industry standards for quality, performance, and compatibility with bolts and other fasteners. These specifications help manufacturers, engineers, and users select appropriate lock nuts for various applications while ensuring reliability and safety in fastening systems.

What is a butt weld elbow? A butt weld elbow is a type of pipe fitting used to change the

At SINO SPECIAL METAL, we provide high-quality butt weld eccentric reducers, essential fittings used in piping systems to seamlessly connect
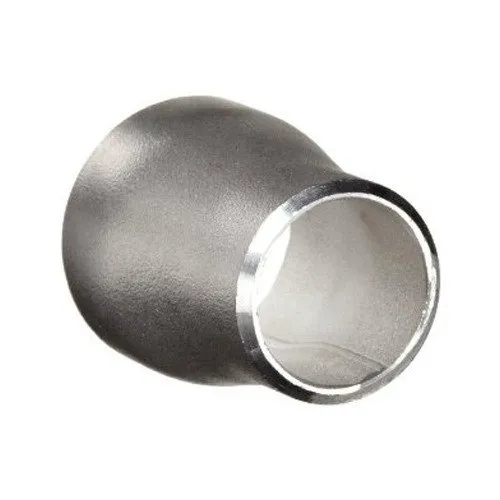

What is a Butt Weld Concentric Reducer At SINO SPECIAL METAL, we offer high-quality butt weld concentric reducers, pivotal components
SSM stands as a premier supplier enterprise, renowned for its specialization in crafting high-quality special metal products. Our commitment to excellence and precision in production ensures that your unique metal requirements are not just met but exceeded. Discover the quality that defines SSM as a leading name in the industry.